Density Mass And Volume Triangle
catronauts
Sep 17, 2025 · 6 min read
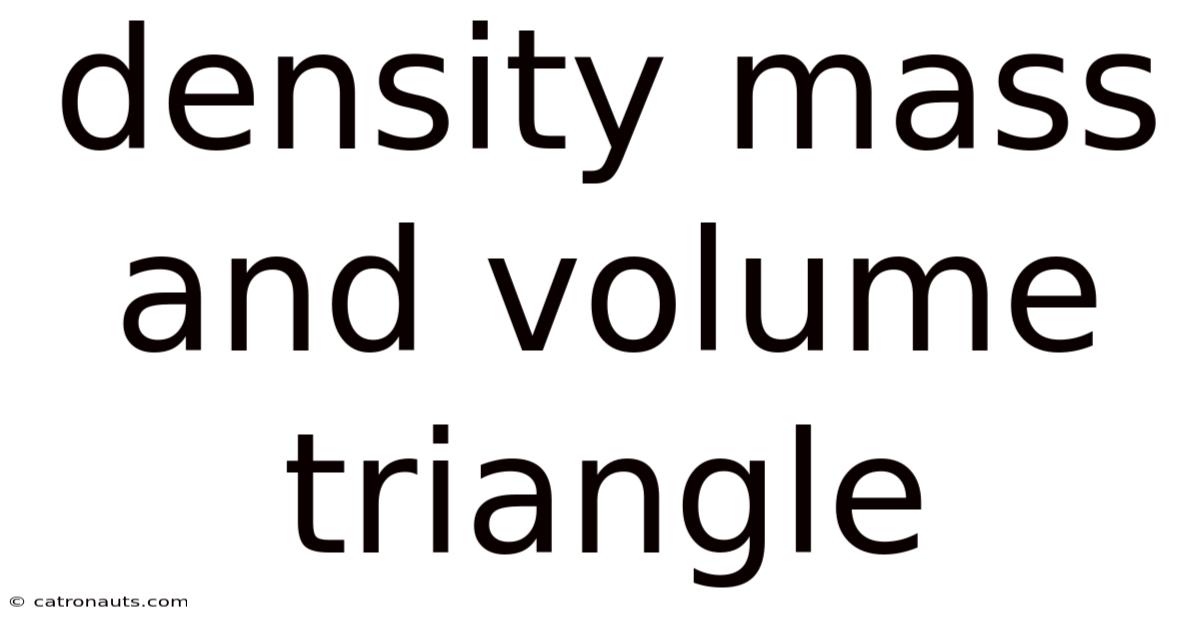
Table of Contents
Understanding the Density, Mass, and Volume Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
The relationship between density, mass, and volume is fundamental in physics and chemistry. Understanding this relationship is crucial for solving a wide range of problems, from determining the composition of materials to designing engineering structures. This comprehensive guide will explore the concept of the "density, mass, and volume triangle," a simple yet powerful tool for visualizing and calculating these interconnected properties. We'll delve into the definitions, formulas, and practical applications, ensuring you gain a thorough understanding of this important concept.
Introduction: The Interplay of Density, Mass, and Volume
Imagine holding a kilogram of feathers and a kilogram of iron. While both have the same mass (the amount of matter), they feel vastly different. This difference is attributed to density, which describes how much mass is packed into a given volume (the amount of space an object occupies). The density, mass, and volume triangle provides a visual representation of this relationship, allowing us to easily calculate any one of these properties if we know the other two.
Think of it like this: mass is the "stuff," volume is the "space it takes up," and density is how much "stuff" is crammed into that "space." A high-density material, like iron, has a lot of mass packed into a small volume. A low-density material, like feathers, has the same mass spread out over a much larger volume.
Defining the Key Terms
Before diving into the triangle, let's clearly define each term:
-
Mass (m): The amount of matter in an object. It's typically measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g). Mass is a measure of inertia – an object's resistance to changes in motion. It remains constant regardless of location.
-
Volume (V): The amount of three-dimensional space occupied by an object. It's typically measured in cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), or liters (L). Volume can change depending on factors like temperature and pressure.
-
Density (ρ): The mass per unit volume of a substance. It's a measure of how tightly packed the matter is. Density is typically measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). Density is often temperature-dependent.
The Density, Mass, and Volume Triangle: A Visual Representation
The density, mass, and volume triangle is a simple diagram that helps visualize the relationship between these three properties. It's constructed as follows:
Density (ρ)
/ \
/ \
Mass (m) --- Volume (V)
The triangle shows that density is the ratio of mass to volume. This can be expressed mathematically as:
ρ = m/V
This formula is the cornerstone of understanding the relationship between these three properties. By rearranging this formula, we can also solve for mass and volume:
- m = ρV (Mass = Density x Volume)
- V = m/ρ (Volume = Mass / Density)
Using the Density, Mass, and Volume Triangle: Practical Examples
Let's illustrate the use of the density, mass, and volume triangle with some practical examples:
Example 1: Finding Density
A block of wood has a mass of 500 grams and a volume of 250 cubic centimeters. What is its density?
Using the formula ρ = m/V, we have:
ρ = 500 g / 250 cm³ = 2 g/cm³
Therefore, the density of the wood is 2 g/cm³.
Example 2: Finding Mass
A container holds 1 liter (1000 cm³) of water. Knowing that the density of water is approximately 1 g/cm³, what is the mass of the water?
Using the formula m = ρV, we have:
m = 1 g/cm³ × 1000 cm³ = 1000 g = 1 kg
Therefore, the mass of the water is 1 kilogram.
Example 3: Finding Volume
A piece of metal with a density of 7.87 g/cm³ has a mass of 157.4 grams. What is its volume?
Using the formula V = m/ρ, we have:
V = 157.4 g / 7.87 g/cm³ ≈ 20 cm³
Therefore, the volume of the metal is approximately 20 cubic centimeters.
Understanding Density Variations: Factors Influencing Density
Density isn't a constant for a given substance. Several factors can affect it:
-
Temperature: As temperature increases, the volume of most substances increases (due to thermal expansion), while the mass remains relatively constant. This leads to a decrease in density. Water is a notable exception, exhibiting its highest density at 4°C.
-
Pressure: Increasing pressure generally leads to a decrease in volume, resulting in an increase in density. This effect is more pronounced in gases than in liquids or solids.
-
Composition: The density of a mixture or solution depends on the densities and proportions of its components. For instance, adding salt to water increases the density of the solution.
-
Phase Changes: The density of a substance changes significantly during phase transitions (solid to liquid, liquid to gas). For example, ice (solid water) is less dense than liquid water.
Applications of Density, Mass, and Volume Calculations
The concept of density, mass, and volume has wide-ranging applications across numerous fields:
-
Material Science: Identifying unknown materials based on their density. Archimedes' principle, based on buoyancy and density, is used in material testing.
-
Engineering: Designing structures and components that can withstand specific loads based on material density and strength.
-
Geology: Determining the composition of rocks and minerals based on their density. This helps in understanding geological formations and resource exploration.
-
Medicine: Density measurements are used in medical imaging techniques (e.g., bone density scans) to diagnose various conditions.
-
Oceanography: Determining water salinity and ocean currents based on variations in water density.
-
Meteorology: Understanding atmospheric pressure and weather patterns which are closely related to air density.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force of gravity acting on that mass. Mass is constant, while weight can vary depending on the gravitational field.
Q2: How do I convert between different units of volume?
You need to use appropriate conversion factors. For example, 1 m³ = 10⁶ cm³ = 1000 L. Remember to maintain consistency in your units throughout your calculations.
Q3: Can density be negative?
No, density cannot be negative. Both mass and volume are always positive quantities.
Q4: What are some common units for density?
Common units include kg/m³, g/cm³, g/mL, and lb/ft³.
Q5: How does the density of a substance relate to its buoyancy?
An object will float if its average density is less than the density of the fluid it's in. If its density is greater, it will sink. This is the principle of buoyancy.
Conclusion: Mastering the Density, Mass, and Volume Triangle
The density, mass, and volume triangle is a fundamental concept in science and engineering. By understanding the relationships between these three properties and mastering the associated formulas, you gain a powerful tool for solving a wide range of problems involving materials, substances, and their properties. Remember that the key is to maintain consistency in your units and to carefully apply the appropriate formula based on the information given. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for further exploration of these important concepts within physics and chemistry. From understanding simple everyday scenarios to solving complex engineering challenges, the ability to calculate and interpret density, mass, and volume is invaluable. Further exploration into related topics such as Archimedes' principle, buoyancy, and specific gravity will further enhance your understanding of these crucial concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does A Circle Have Sides
Sep 17, 2025
-
Pyramid With Rectangular Base Volume
Sep 17, 2025
-
Is A Gem A Diamond
Sep 17, 2025
-
Characters Of Commedia Dell Arte
Sep 17, 2025
-
Language Of The Solomon Islands
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Density Mass And Volume Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.